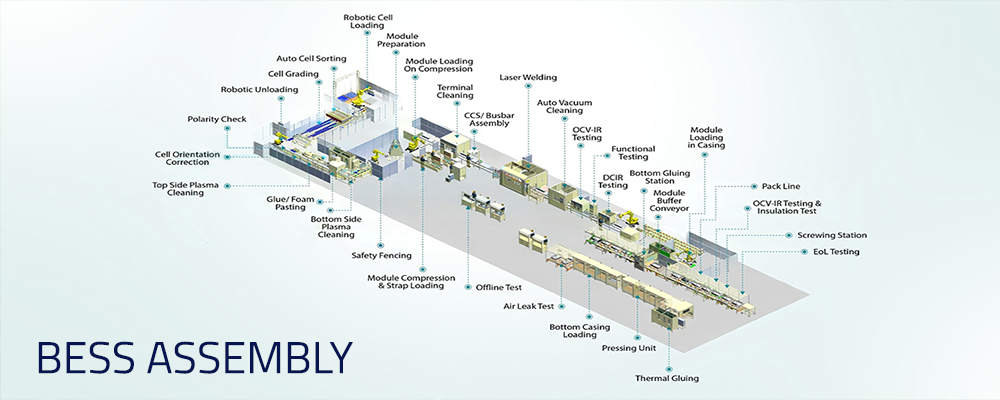
BESS Assembly
1. Inbound QC: Rigorous testing of incoming cells/modules (voltage, internal resistance, capacity sampling).
2. Module Assembly (Phase 2+): Automated cell sorting -> Laser/Ultrasonic busbar welding -> Slave BMS mounting -> Module casing.
3. Rack Integration: Mounting modules onto racks, connecting wiring harnesses, and communication cables (CAN bus).
4. Containerization:
- Installation of racks using overhead cranes.
- Integration of PCS, step-up transformer, switchgear, and control panels.
- Installation of HVAC and fire suppression systems (e.g., Novec 1230 / FM-200).
5. System-Level FAT:
- High-voltage system interlocking and safety checks.
- End-to-end communication tests (BMS -> PCS -> EMS -> SCADA).
- Controlled charge-discharge cycle tests using grid simulators or resistive/reactive load banks.
- High-Potential (Hipot) insulation testing.